Discover quality.
These gaskets are therefore described as being semi-detachable, as the welded sealing joint needs to be undone as well as the flange bolts.
Weld ring gaskets are generally made of the same or a related material as the pipe or flange and are only used in pairs.
The choice between the various profiles depends on the operating conditions of the weld ring gasket. The table shows the typical features of Profiles A21 to A25. The ‘attachment seam’ is the connection of a welded half with the flange. The ‘attachment seam’ can be located internally or externally. The ‘seal seam’ is always the welding of both weld rings with one another.
The suitability of the materials for welding (gasket to flange), the ability to weld (proper fitting) and the security of the welding (expert layout and specifications) should be assessed and tested with regard to the local operating conditions by an expert welding engineer. The ”attachment seams“ and ”seal seam“ should be arranged so that they can withstand all load conditions.
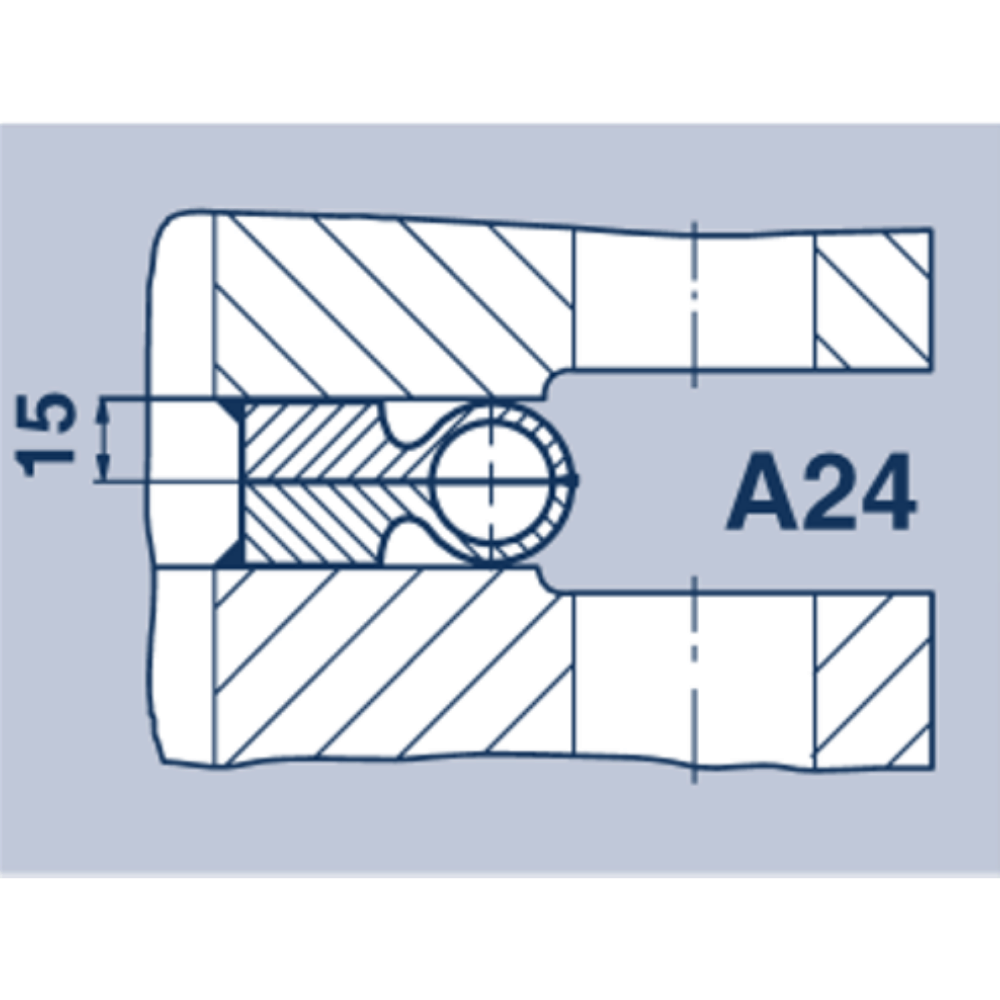
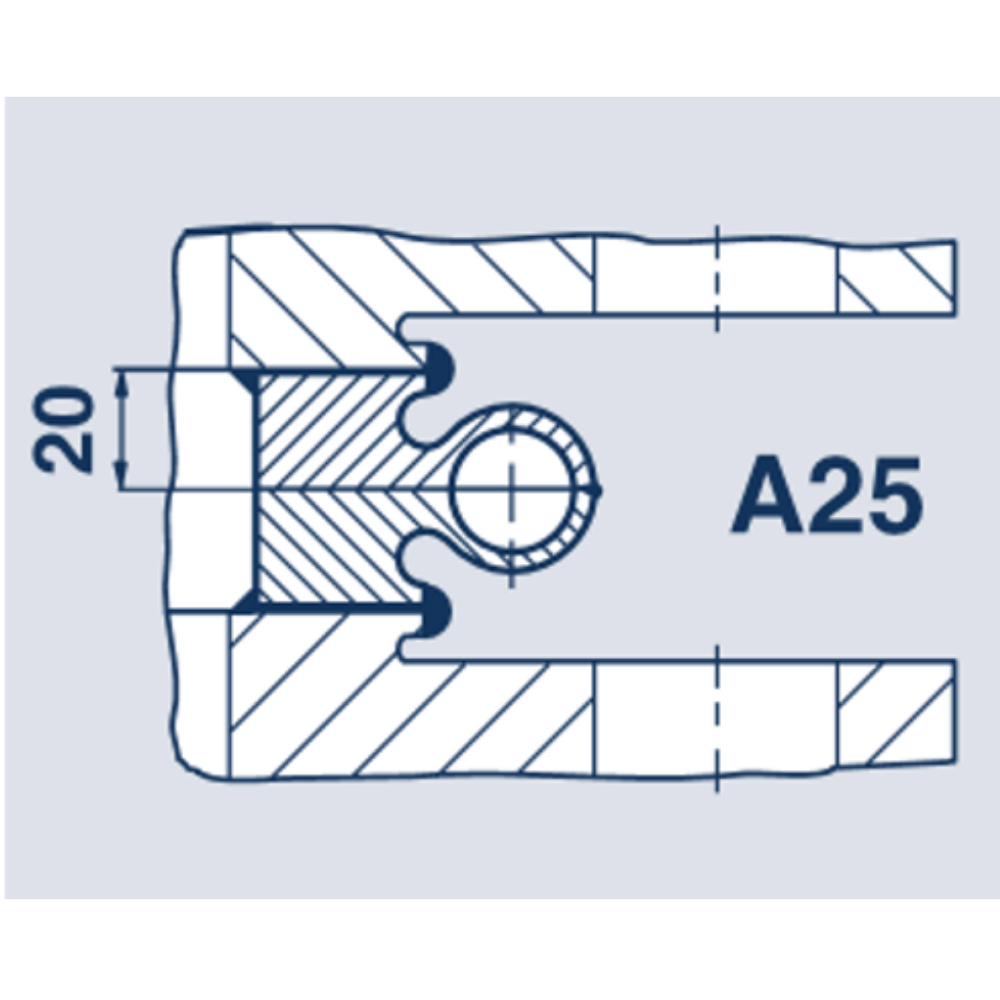
Weld rings with hollow lips in Profiles A24, A25 and A23 optimise the stress ratio in the seal seam. Weld rings with hollow lips are recommended for use when connecting components with different heat exchange properties.
The advantage of weld ring gaskets in Profile A24 and A25 lies in their greater motion absorption. They are predominantly used with heat exchangers with differing radial strain properties, e.g. as gaskets between channel flanges and tube plates. With the A24 gasket the weld seams are not accessible from the outside. However in many cases this is an advantage, particularly where creep corrosion is feared
| Profile | Internal ”attachment seam“ Crevice corrosion between weld ring and flange is avoided | External “attachment seam” Re-welding or disassembly possible | Capacity of radia differential expansion | Undo and re-weld |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Usual | Not possible |
Depending on the thickness of the wall of the tours, to a max. △r - 5 mm | Easy to separate with a 2 mm cutting wheel. Can be re-welded 2 to 4 times. |
 | Possible to have additional attachment. Intermittently welded. | Usual |
Depending on the thickness of the wall of the torus, to a max. △r - 5 mm | Easy to separate with a 2 mm cutting wheel. Can be re-welded 2 to 4 times. |
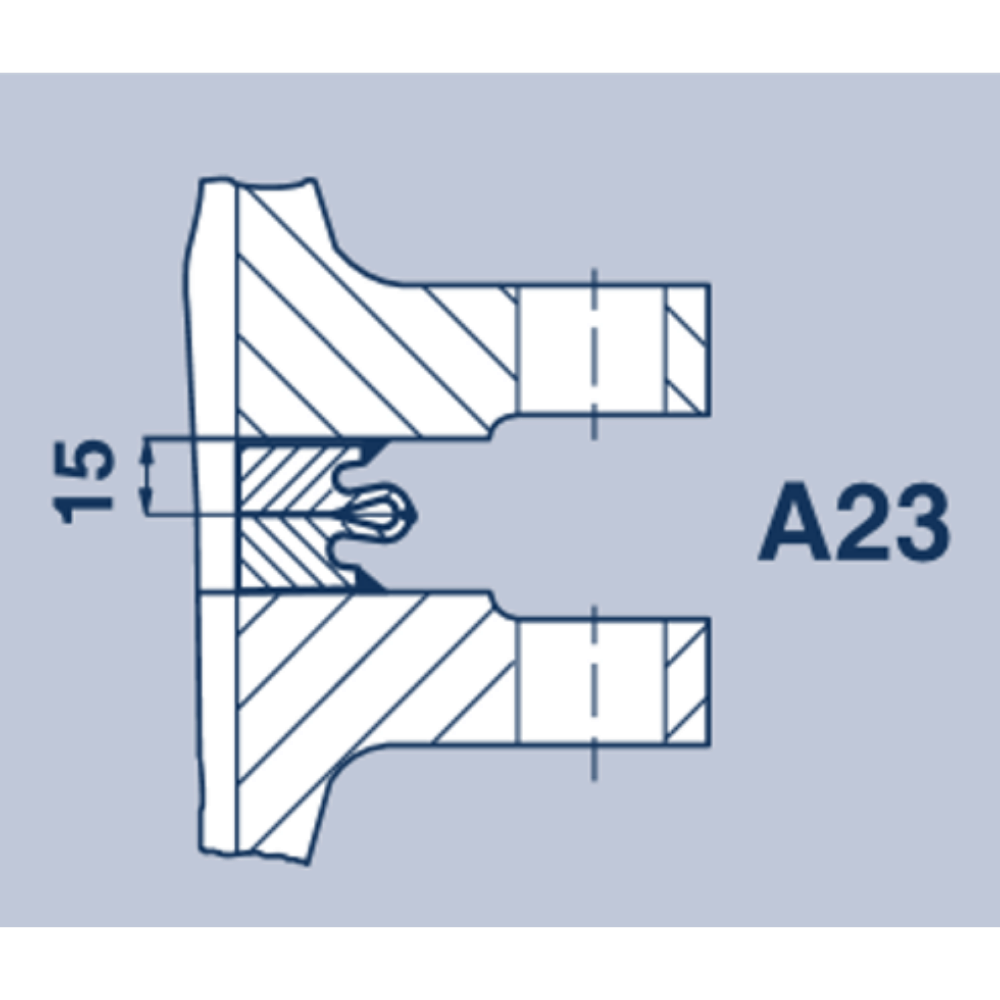 | a) Only as an additional attachment. Intermittently welded. b) If there is a danger of corrosion. | a) Usual setup. b) Only as an additional attachment aid. Intermittently welded. | Only low capacity due to the small lip. max. △r - 5 mm | Difficult to separate Can be re-welded 1 to 3 times. |
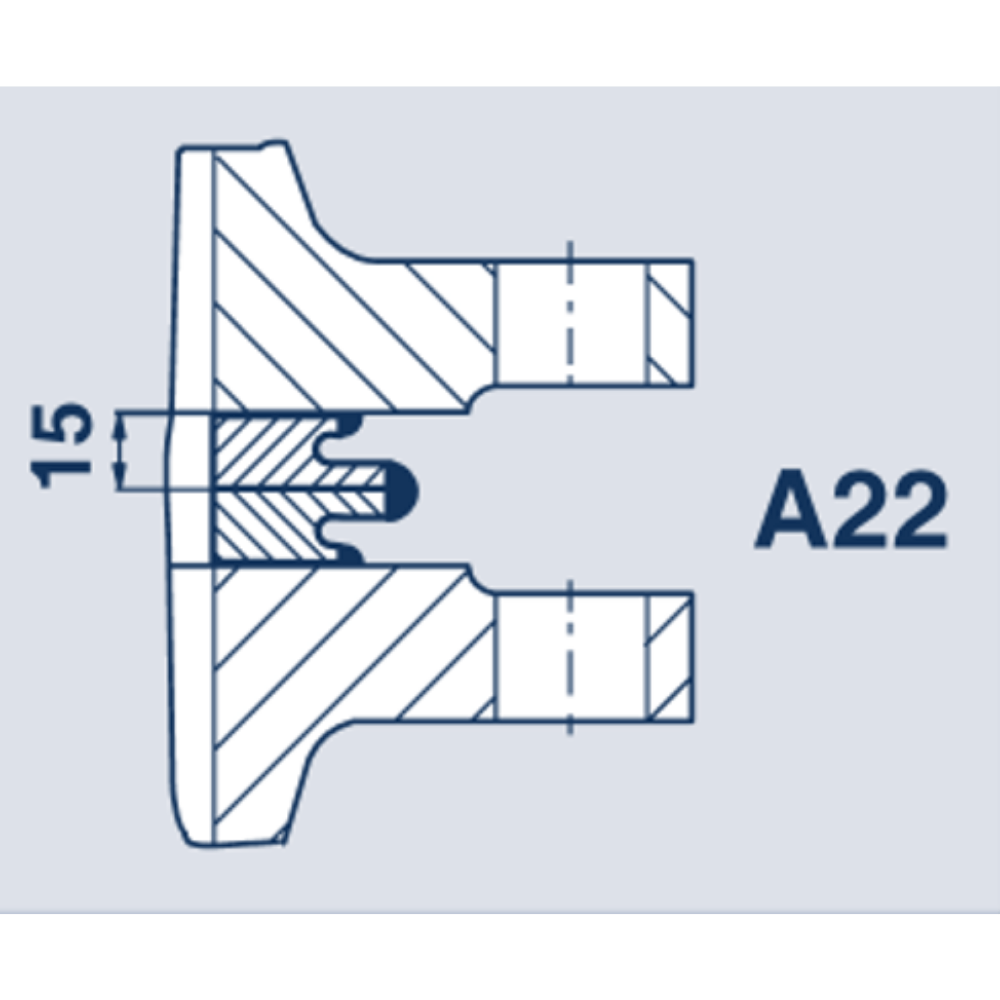 | a) Only as an additional attachment. Intermittently welded. b) If there is a danger of corrosion. | a) Usual setup. b) Only as an additional attachment aid. Intermittently welded. | Not really possible
max. △r - 0.1 mm | With cutting wheel Separation loss 2 to 3 mm respectively. Can be re-welded 3 to 5 times. |
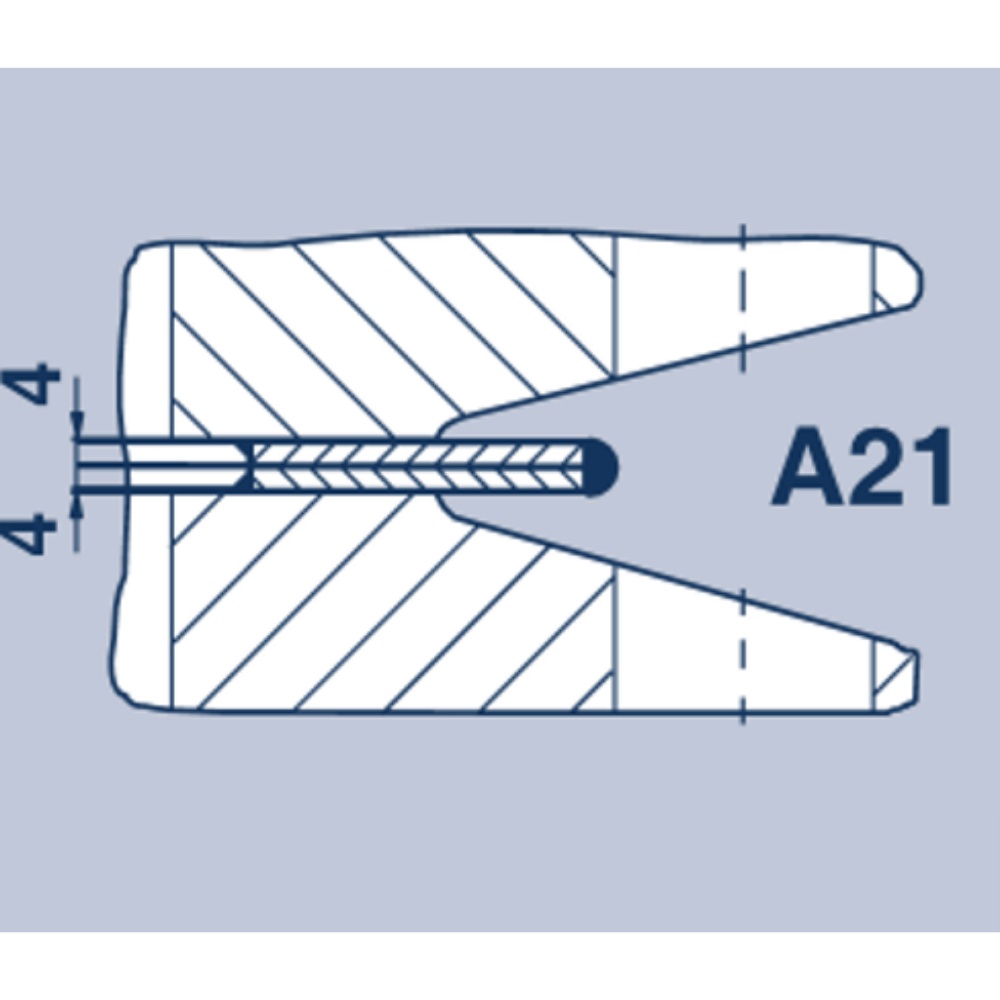 | Usual | Not possible Flange form M in accordance with DIN 2526 also necessary. | Modest capacity
Depending on projection. max .△r - 0.3 mm | With cutting wheel Separation loss 2 to 3 mm respectively. Can be re-welded 2 to 4 times. |
All weld ring gaskets can be combined with additional auxiliary gaskets. These can be useful for various different reasons.
Weld ring gaskets should be fitted so that the weld ring halves lie on top of each other, and parallel to each other and to the flanges.
If weld ring gaskets are used with auxiliary gaskets, the flange and bolt calculations must be carried out once for the weld ring gasket with the seal diameter to the outermost seal seam and once for the auxiliary gasket.
With the use of auxiliary gaskets, a gap of 0.3 mm remains between the weld ring gasket halves, depending on the design.

KLINGER has been the world’s leading manufacturer and provider of industrial sealing, fluid control and fluid monitoring systems for more than 130 years.
KLINGER Mzansi (Pty) Ltd | KLINGER (Pty) Ltd | KLINGER Zambia Ltd